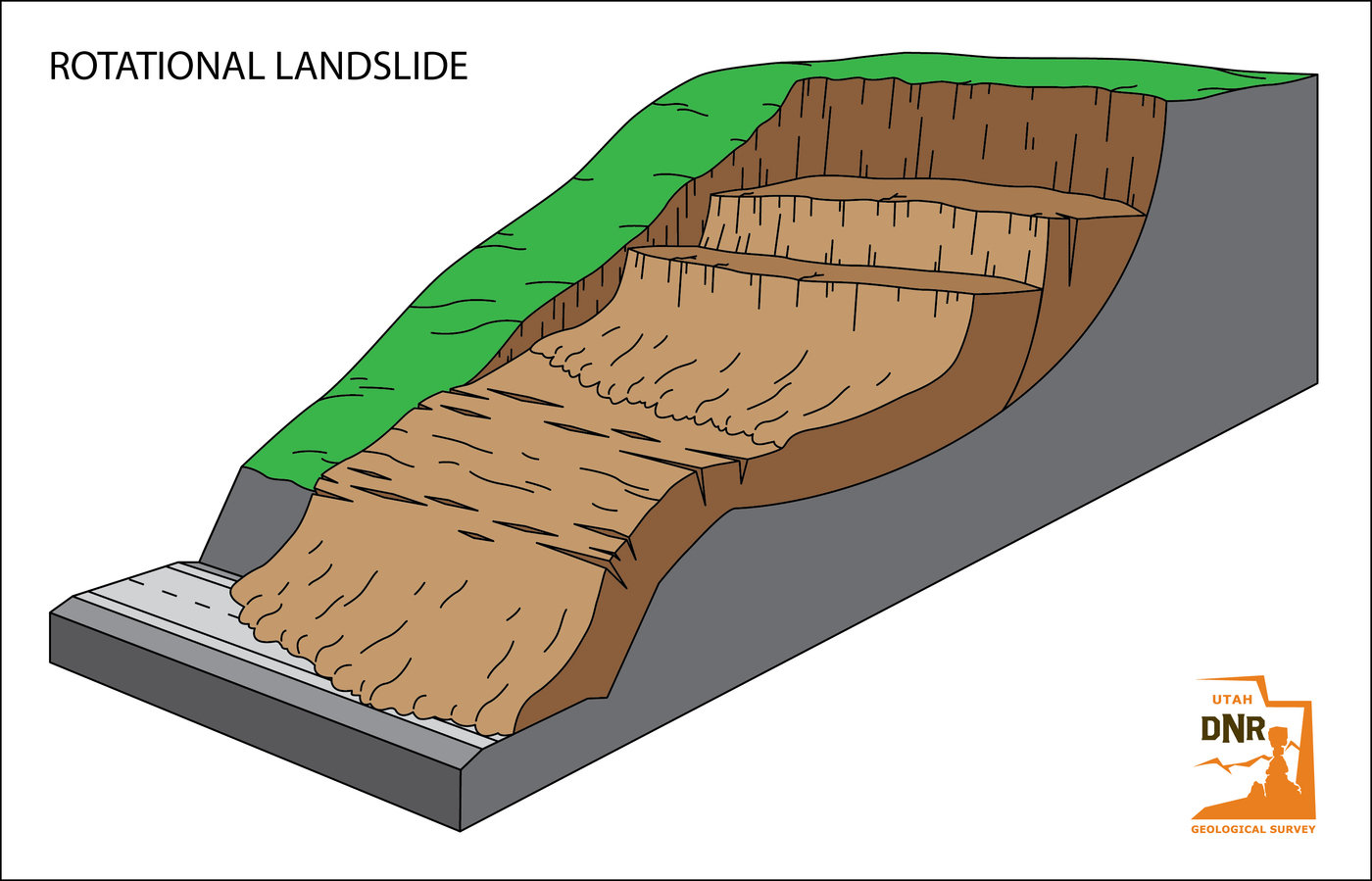
↪ WHAT IS A LANDSLIDE? ↩
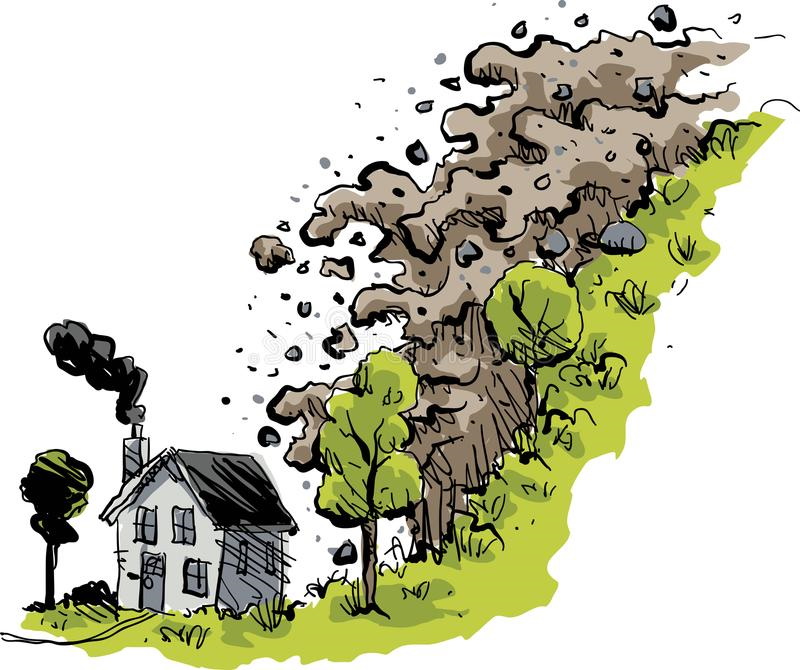
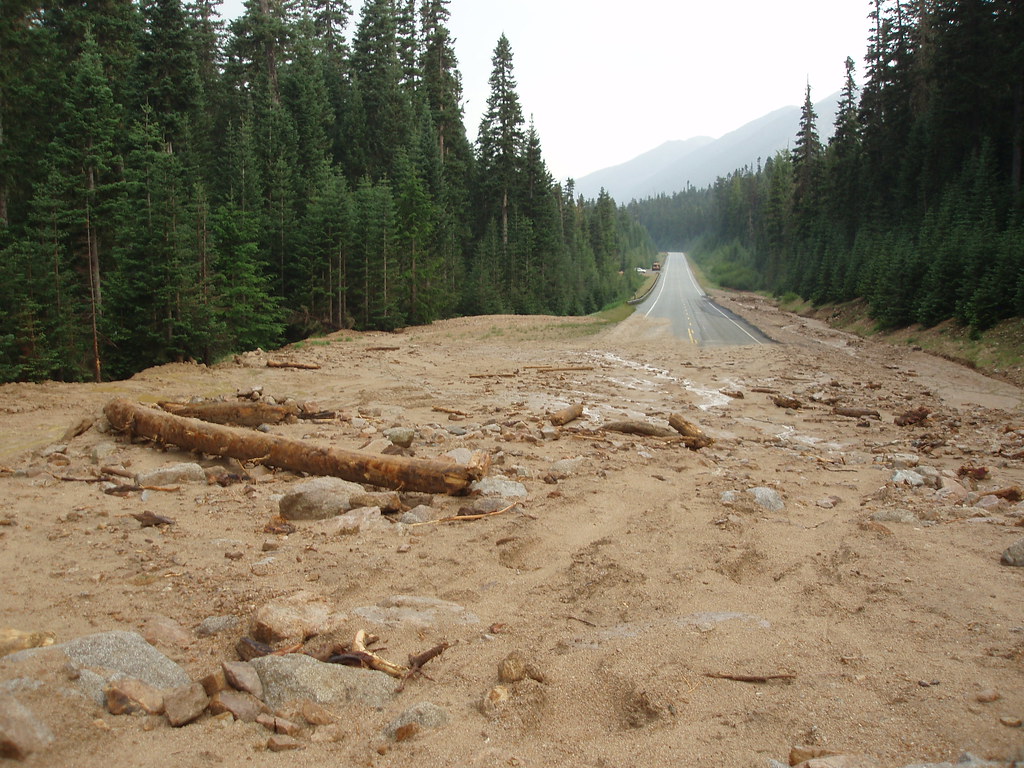
LANDSLIDES is a movement of mass rock, debrisor earth down a slope due to gravity. The materials may move by falling, toppling, sliding, spreading, or flowing. When soil, rock, and other earth debris can no longer hold it together and gives way to gravity, landslides happen. Earthquake shaking and other factors can also induce landslides underwater causing tidal waves and damage to coastal areas. These landslides are called submarine landslides. Submarine landslides sometimes cause tsunamis that damage coastal areas. Volcanic landslides, also called lahars, are among the most devastating type of landslides.
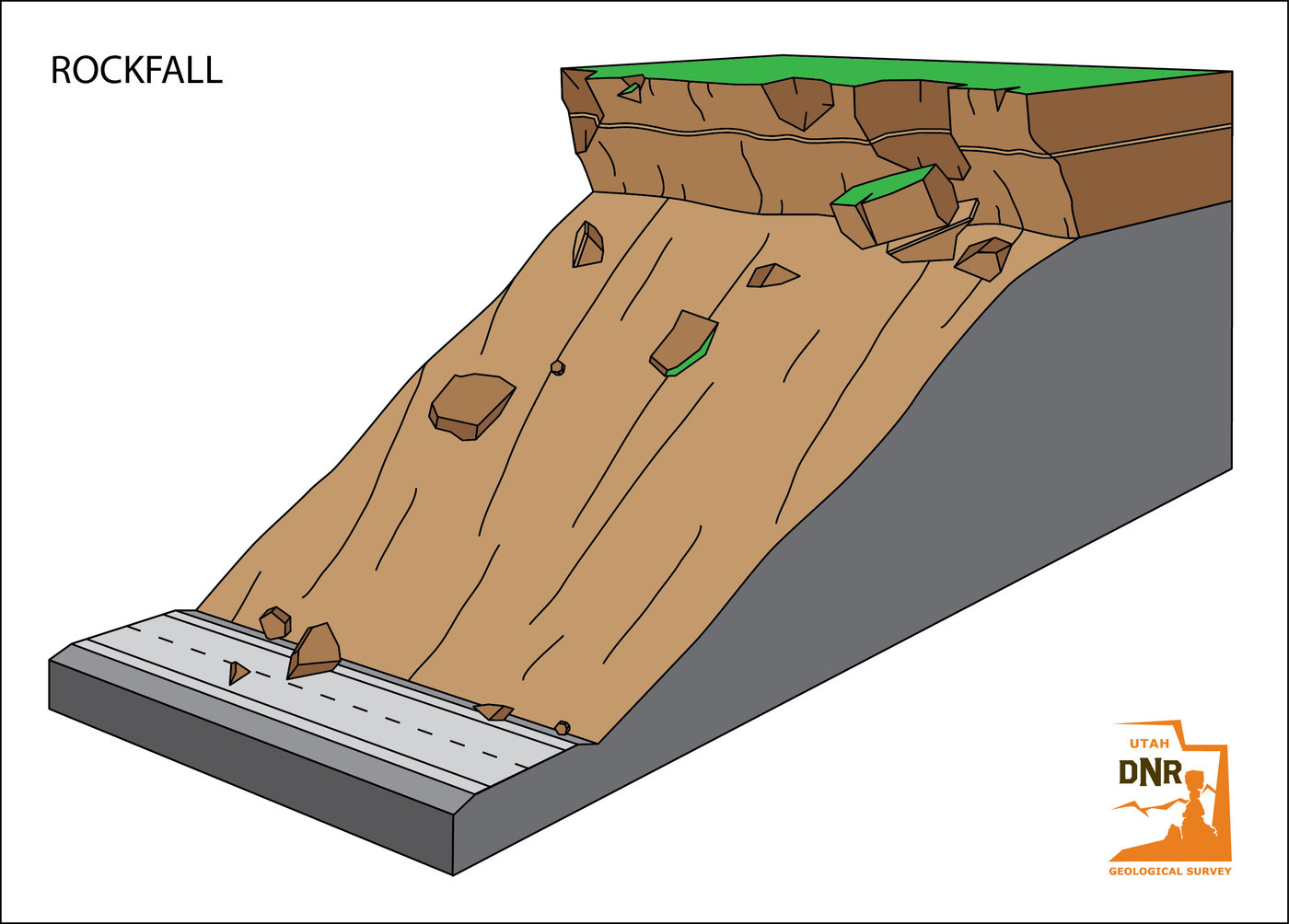
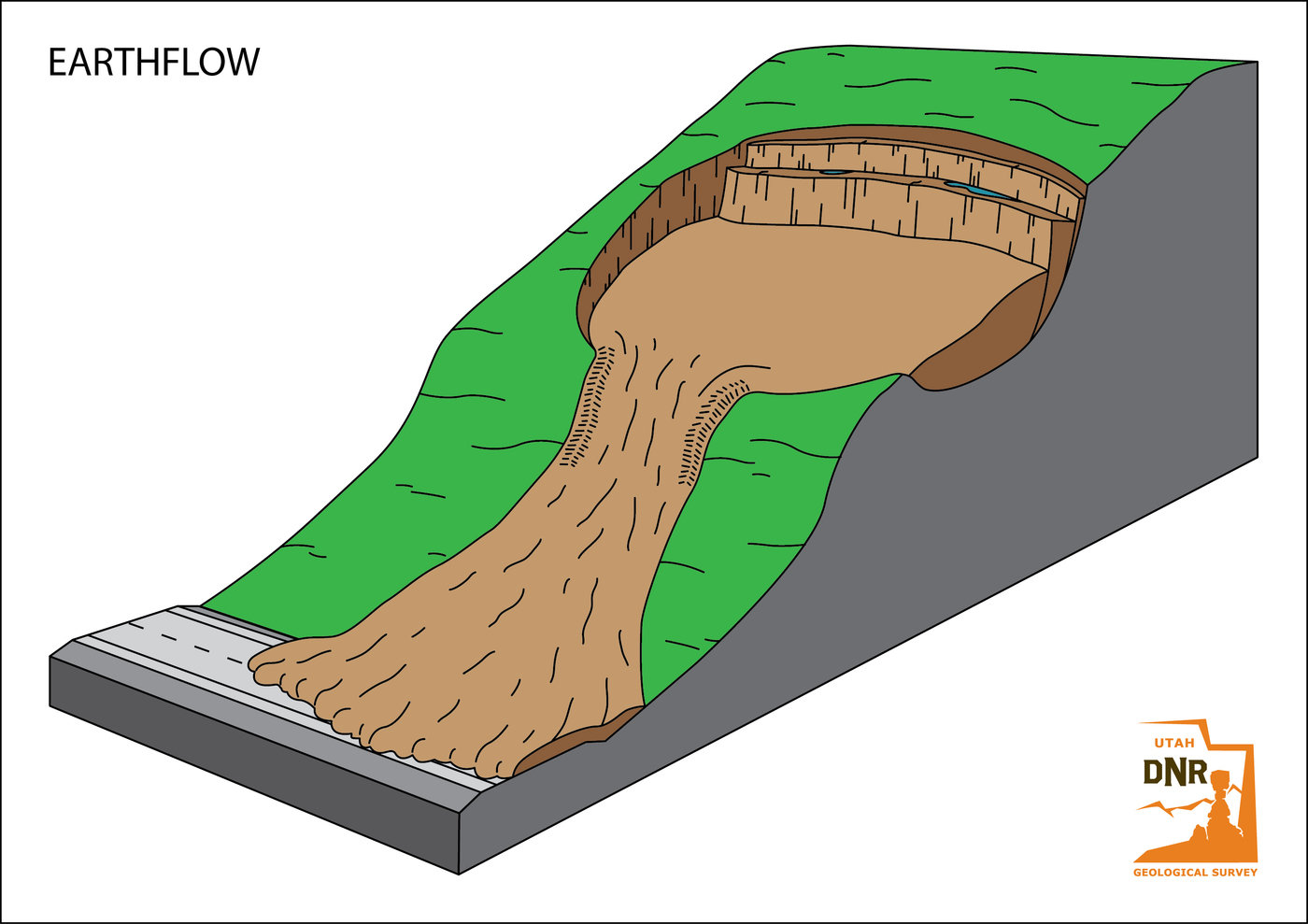
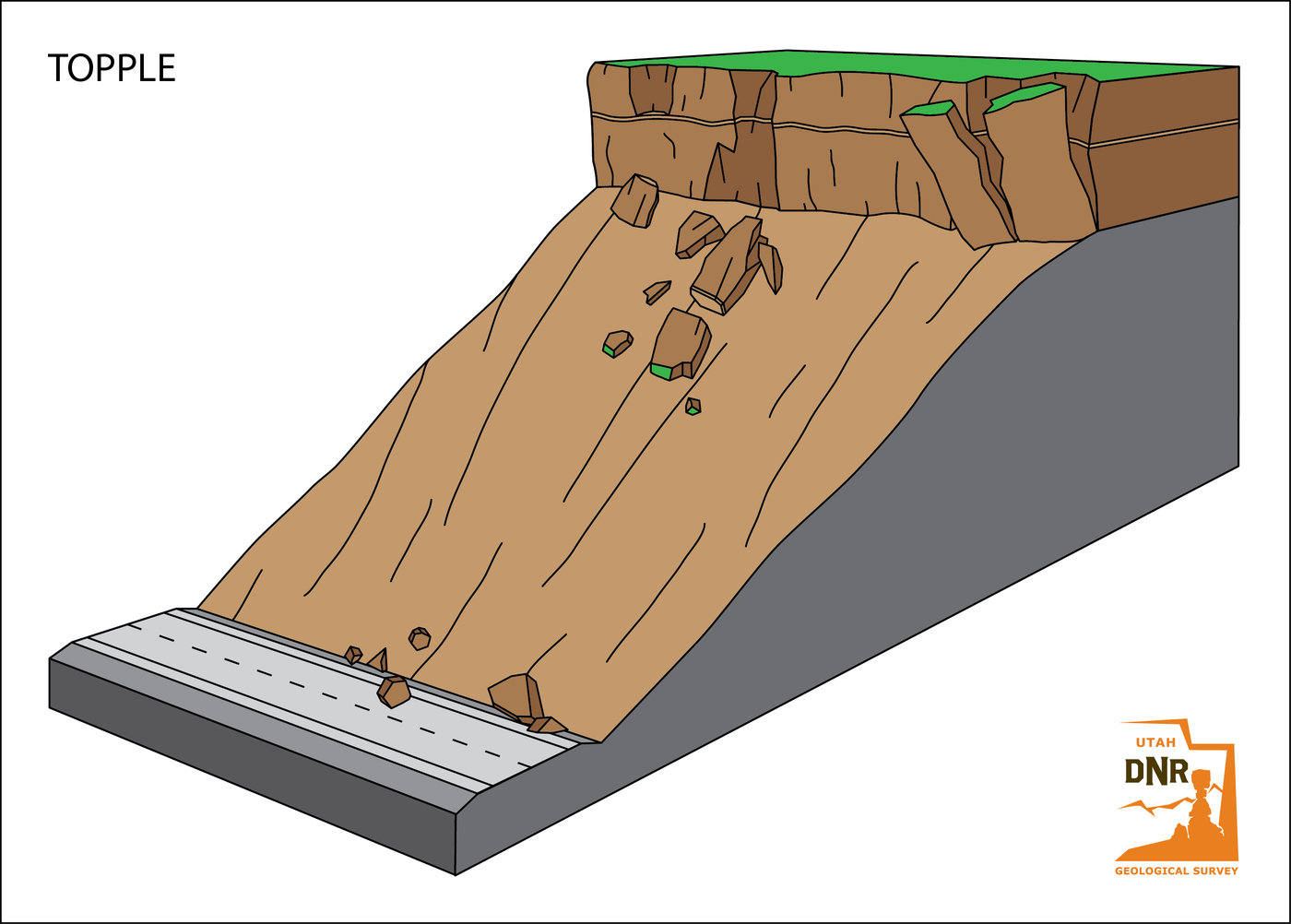
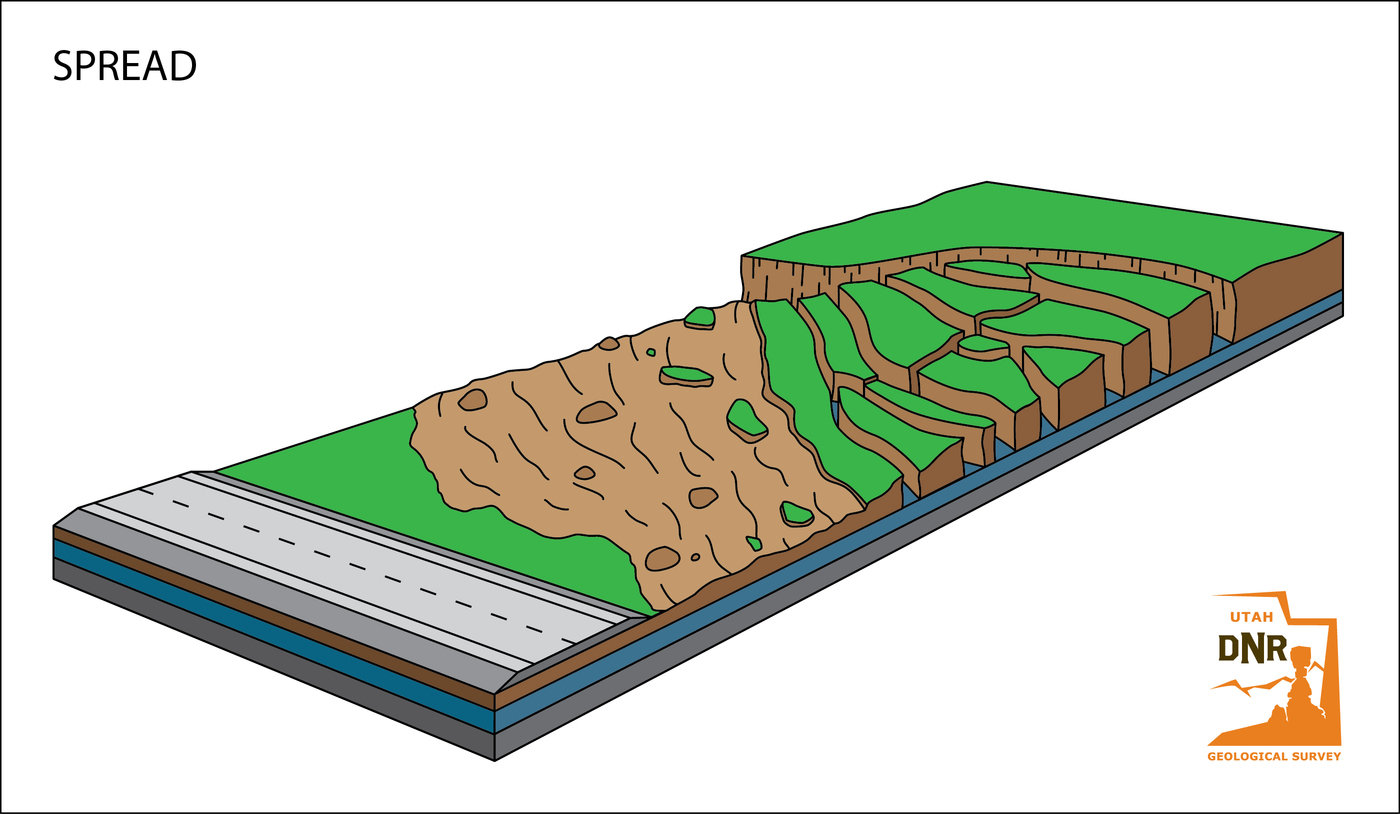
GEOLOGISTS, scientists who study the physical formations of the Earth, sometimes describe landslides as one type of mass wasting. A mass wasting is any downward movement in which the Earth's surface is worn away. Other types of mass wasting include rockfalls and the flow of shore deposits called alluvium.
The Philippines is an example of a country that is prone to landslides. According to the MGB, up to 80 percent of the country's total land area is landslide prone, making the country the fourth most exposed to landslide risk, after Indonesia, India and China. More than 100,000 people are exposed in the Philippines, according to the UN International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR).
a. Weak or sensitive materials
b. Weathered materials
c. Sheared, jointed, or fissured materials
d. Adversely oriented discontinuity (bedding, schistosity, fault, unconformity, contact, and so forth)
e. Contrast in permeability and/or stiffness of materials
a. Tectonic or volcanic uplift
b. Glacial rebound
c. Fluvial, wave, or glacial erosion of slope toe or lateral margins
d. Subterranean erosion (solution, piping)
e. Deposition loading slope or its crest
f. Vegetation removal (by fire, drought)
g. Thawing
h. Freeze-and-thaw weathering
i. Shrink-and-swell weathering
a. Excavation of slope or its toe
b. Loading of slope or its crest
c. Drawdown (of reservoirs)
d. Deforestation
e. Irrigation
f. Mining
g. Artificial vibration
h. Water leakage from utilities
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION :
DID YOU KNOW?
The largest subaerial (on land) landslide in Earth's recorded history was connected with the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens volcano in Washington state, USA. That landslide had a volume of 2.8 cubic kilometers (0.67 cubic miles) of material and the landslide traveled about 22.5 kilometers (14 miles) down the North Fork Toutle River. Average landside depth was 46 meters (150 feet) with a maximum depth of 182 meters (600 feet). The landslide velocity was 112-240 kilometers per hour (70-150 miles per hour).
Some landslides move at many meters per second, while others creep along at an centimeter or two a year. The amount of water, ice, or air in the earth should also be considered. Some landslides include toxic gases from deep in the Earth expelled by volcanoes. Some landslides, called mudslides, contain a high amount of water and move very quickly. Complex landslides consist of a combination of different material or movement types.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF LANDSLIDES
HOW CAN WE MITIGATE A LANDSLIDE?
Landslides are being mitigated significantly, with the use of geometrical steps that adjust the geometry of the hillside (in general the slope). Hydrogeological techniques for the reduction of groundwater levels or the reduction of the material's water content. Chemical and mechanical methodology in which efforts are made to increase the shear strength of the instability mass or to incorporate active external forces (anchors, rock or earth nailing) to counteract the destabilizing forces or passive forces (structural wells, towers or hardened soil).
Stability increases when ground water is prevented from rising in the landslide mass by (1) covering the landslide with an impermeable membrane, (2) directing surface water away from the landslide, (3) draining ground water away from the landslide, and (4) minimizing surface irrigation. Slope stability is also increased when a retaining structure and/or the weight of a soil/rock berm are placed at the toe of the landslide or when mass is removed from the top of the slope.
Make an Emergency Plan: Create a family emergency communications plan that has an out-of-state contact. Plan where to meet if you get separated. Make a supply kit that includes enough food and water for several days, a flashlight and a whistle. Don’t forget to include your pet in your emergency plan. Remember that some evacuation shelters do not accept pets. Click here to know how to make an emergency plan
Build an emergency kit with the supplies you will need if you have to quickly evacuate your home. Gather supplies, including non-perishable foods, cleaning supplies, and water for several days, in case you must leave immediately. It is recommended that there is at least 3 days’ worth of supplies on hand, including one gallon per day for each person and pet. Click here to know how to make an emergency kit
WHAT DO I NEED TO DO TO SURVIVE A LANDSLIDE?
Become familiar with the land around you. Learn whether landslides occur in your area by contacting local officials. Debris flows can start in places they’ve never been and return to slops where they’ve already been.
Prepare for landslides by following proper land-use procedures - avoid building near steep slopes, close to mountain edges, near drainage ways or along natural erosion valleys.
You can't stop or change the path of a debris flow. However, you may be able to protect your property from floodwaters or mud by use of sandbags, retaining walls or k-rails (Jersey barriers)
Be aware that when a flow is big enough, it goes where it pleases. If you divert a flow and it flows on a neighbor’s property, you may be liable for damages. In mud and debris flow areas, consider building channels or deflection walls to try to direct the flow around buildings.
If you suspect imminent danger, evacuate immediately. Inform affected neighbors if you can, and contact your public works, fire or police department.
Listen for unusual sounds that might indicate moving debris, such as trees cracking or boulders knocking together.
If you are near a stream or channel, be alert for any sudden increase or decrease in water flow and notice whether the water changes from clear to muddy. Such changes may mean there is debris flow activity upstream so be prepared to move quickly.
Be especially alert when driving— watch for collapsed pavement, mud, fallen rocks and other indications of possible debris flow.
Take your pet/animals with you when you are ordered or decide to evacuate.
Consider a precautionary evacuation of large or numerous animals as soon as you are aware of impending danger.
Listen to authorities for information and instructions. Return home only when authorities say it is safe. Pay attention to all warnings and evacuation notices.
Report broken utility lines and damaged roadways and railways to appropriate authorities. Reporting potential hazards will get the utilities turned off as quickly as possible, preventing further hazard and injury.
Check for injured and trapped people near the slide, without entering the direct slide area. Direct rescuers to their locations.
Help a neighbor who may require special assistance - infants, elderly people, and people with disabilities. Elderly people and people with disabilities may require additional assistance. People who care for them or who have large families may need additional assistance in emergency situations.
EMERGENCY HOTLINES
911
Truck Lines :
911-506162636465
Operations Center :
(02) 8911-1406
(02) 8912-2665
(02) 8912-5668
(02) 8911-1873
Truck lines :
(02) 8931-8101 to 07
Disaster Response Unit :
(02) 8856-3665
(02) 8852-8081
Text Hotline :
0918-912-2813
Hotline :
143
Disaster Management Office :
132 (Manager)
133 (Radio Room)
134 (Staff)
Emergency Hotline :
117
(02) 8722-0650
Text Hotline :
0917-847-5757
Direct Line :
(02) 8426-0219
(02) 8426-0246
REFERENCES & ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Landslides & Debris Flow | Ready.gov (2020) Retrieved 11 October 2020, https://www.ready.gov/landslides-debris-flow
Landslides. (2020). Retrieved 19 October 2020, from http://disastercenter.com/New%20Guide/Landslides.html#:~:text=Gravity%20is%20generally%20the%20force,earthquake%20shaking%2C%20and%20volcanic%20eruptions.
What was the largest landslide in the United States? In the world?. (2020). Retrieved 19 October 2020, from https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-was-largest-landslide-united-states-world?qt-news_science_products=0#qt-news_science_products
Landslides and Mudslides - The Official Allied Universal Fire Life Safety Training Blog. (2018). Retrieved 19 October 2020, from https://rjwestmore.com/2018/08/3279/3279/
Unveil WHY Landslides Occur. (2020). Retrieved 19 October 2020, from https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/f11400b49d814766ad9f4b418094e2a1
Slump | geology. (2020). Retrieved 19 October 2020, from https://www.britannica.com/science/slump
Usgs.gov. (2021). Landslide Preparedness. [online] Available at: https://www.usgs.gov/natural-hazards/landslide-hazards/science/landslide-preparedness?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects [Accessed Oct. 2020].
Weatherwizkids.com. (2020). Landslides | Weather Wiz Kids. [online] Available at: http://www.weatherwizkids.com/?page_id=1326 [Accessed Oct. 2020].
Live Science Staff (2012). What is a Landslide? [online] Livescience.com. Available at: https://www.livescience.com/amp/32373-what-is-a-landslide.html [Accessed Oct. 2020].
National Geographic Society (2014). landslide. [online] National Geographic Society. Available at: https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/landslide/ [Accessed Oct. 2020].
Landslides. (2020). TYPES OF LANDSLIDES. [online] Available at: https://monstrouslandslides.weebly.com/types-of-landslides.html [Accessed Oct. 2020].
ReliefWeb. (2010). PHILIPPINES: Landslide risk increasing - Philippines. [online] Available at: https://reliefweb.int/report/philippines/philippines-landslide-risk-increasing [Accessed Oct. 2020].